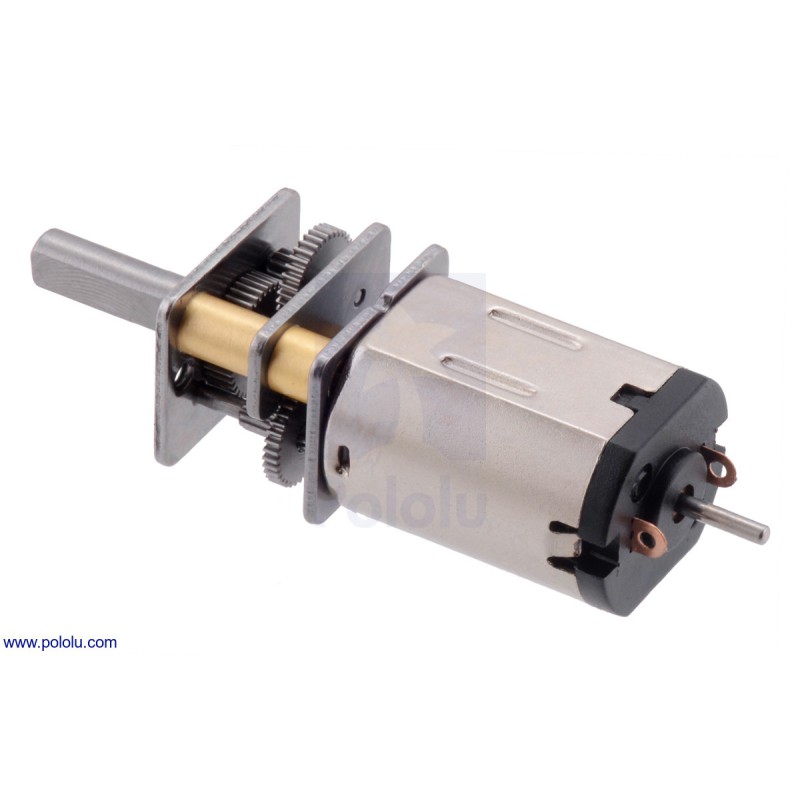
380:1 Micro Metal Gearmotor HPCB 6V with Extended Motor Shaft
This gearmotor is a miniature high-power, 6V brushed DC motor with long-life carbon brushes and a 379.17:1 metal gearbox. This version has stainless steel gearbox plates instead of the standard brass ones for increased durability and resistance to wear from radial loads. It has a cross section of 10×12mm, and the D-shaped gearbox output shaft is 9mm long and 3mm in diameter. This version also has a 4.5×1mm extended motor shaft.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 85 RPM, 100 mA |
5.0 kg⋅cm (69 oz⋅in), 1.5 A |
These tiny brushed DC gearmotors are available in a wide range of gear ratios—from 5:1 up to 1000:1—and with five different motors: high-power 6V and 12V motors with long-life carbon brushes (HPCB), and high-power (HP), medium power (MP), and low power (LP) 6V motors with shorter-life precious metal brushes. The 6V and 12V HPCB motors offer the same performance at their respective nominal voltages, just with the 12V motor drawing half the current of the 6V motor. The 6V HPCB and 6V HP motors are identical except for their brushes, which only affect the lifetime of the motor.
The HPCB versions can be differentiated from versions with precious metal brushes by their copper-colored terminals. Note that the HPCB terminals are 0.5mm wider than those on the other micro metal gearmotor versions (2mm vs. 1.5mm), and they are about 1mm closer together (6mm vs. 7mm).
Versions of these gearmotors are also available with an additional 1mm-diameter output shaft that protrudes from the rear of the motor. This 4.5mm-long rear shaft rotates at the same speed as the input to the gearbox and offers a way to add an encoder, such as our magnetic encoder for micro metal gearmotors (see the picture on the right), to provide motor speed or position feedback.
With the exception of the 1000:1 gear ratio versions, all of the micro metal gearmotors have the same physical dimensions, so one version can be easily swapped for another if your design requirements change.
Please see the micro metal gearmotor datasheet (2MB pdf) for more information, including detailed performance graphs for each micro metal gearmotor version. You can also use our dynamically sortable micro metal gearmotor comparison table for search for the gearmotor that offers the best blend of speed, torque, and current-draw for your particular application.
Note: Stalling or overloading gearmotors can greatly decrease their lifetimes and even result in immediate damage. The recommended upper limit for instantaneous torque is 2.5kg-cm (35oz-in) for the 380:1 and 1000:1 gearboxes, and 2kg*cm (25oz-in) for all the other gear ratios; we strongly advise keeping applied loads well under this limit. Stalls can also result in rapid (potentially on the order of seconds) thermal damage to the motor windings and brushes, especially for the versions that use high-power (HP and HPCB) motors; a general recommendation for brushed DC motor operation is 25% or less of the stall current.
In general, these kinds of motors can run at voltages above and below their nominal voltages; lower voltages might not be practical, and higher voltages could start negatively affecting the life of the motor.
Details for item #4797
Exact gear ratio:
This gearmotor is a miniature high-power, 6V brushed DC motor with long-life carbon brushes and a 379.17:1 metal gearbox. This version has stainless steel gearbox plates instead of the standard brass ones for increased durability and resistance to wear from radial loads. It has a cross section of 10×12mm, and the D-shaped gearbox output shaft is 9mm long and 3mm in diameter. This version also has a 4.5×1mm extended motor shaft.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 85 RPM, 100 mA | 5.0 kg⋅cm (69 oz⋅in), 1.5 A |
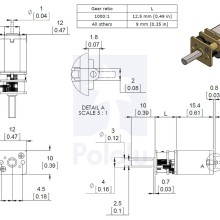
Gearmotor Dimensions
In terms of size, these gearmotors are very similar to Sanyo’s popular 12mm NA4S DC gearmotors, and gearmotors with this form factor are occasionally referred to as N20 motors. The versions with carbon brushes (HPCB) have slightly different terminal and end-cap dimensions than the versions with precious metal brushes, but all of the other dimensions are identical.
Dimensions
| Size: | 10 × 12 × 26 mm1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 9.5 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 3 mm2 |
General specifications
| Gear ratio: | 379.17:1 |
|---|---|
| No-load speed @ 6V: | 85 rpm |
| No-load current @ 6V: | 0.10 A |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 1.5 A |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 5.0 kg·cm |
| Max output power @ 6V: | 1.1 W |
| Extended motor shaft?: | Y |
| Long-life carbon brushes?: | Y |
| Motor type: | 1.5A stall @ 6V (HPCB 6V - carbon brush) |
Performance at maximum efficiency
| Max efficiency @ 6V: | 30 % |
|---|---|
| Speed at max efficiency: | 68 rpm |
| Torque at max efficiency: | 1.0 kg·cm |
| Current at max efficiency: | 0.40 A |
| Output power at max efficiency: | 0.71 W |
Notes:
File downloads
- Datasheet for Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors (2MB pdf)
-
- Dimension diagrams of Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors (262k pdf)
-
- 3D model of a Micro Metal Gearmotor with Extended Motor Shaft and a #1086 bracket (4MB step)
- 3D model of a Micro Metal Gearmotor with Extended Motor Shaft and a #1086 bracket (or #989 bracket, which is just a black version of the #1086).
- 3D model of a Micro Metal Gearmotor and a #1086 bracket (4MB step)
- 3D model of a Micro Metal Gearmotor and a #1086 bracket (or #989 bracket, which is just a black version of the #1086).
- 3D model of Micro Metal Gearmotors (single-shaft, precious metal brushes, not 1000:1) (11MB step)
- 3D model of low-power, medium-power, high-power Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors. This diagram does not apply to the HPCB versions, dual-shaft versions, or 1000:1 gear ratios.
- 3D model of Micro Metal Gearmotors with extended motor shafts (precious metal brushes, not 1000:1) (11MB step)
- 3D model of low-power, medium-power, high-power Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors with extended motor shafts. This diagram does not apply to the HPCB versions, single-shaft versions, or 1000:1 gear ratios.
- 3D model of 1000:1 Micro Metal Gearmotors (single-shaft, precious metal brushes) (14MB step)
- 3D model of Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors with 1000:1 gearboxes. This diagram does not apply to the HPCB versions, dual-shaft versions, or other gear ratios.
- 3D model of 1000:1 Micro Metal Gearmotors with extended motor shafts (precious metal brushes) (14MB step)
- 3D model of Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors with 1000:1 gearboxes and extended motor shafts. This diagram does not apply to the HPCB versions, single-shaft versions, or other gear ratios.
- 3D model of HPCB Micro Metal Gearmotors (single-shaft, carbon brushes, not 1000:1) (11MB step)
- 3D model of high-power carbon brush (HPCB) Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors. This diagram does not apply to precious metal brush (i.e. non-HPCB) versions, dual-shaft versions, or 1000:1 gear ratios.
- 3D model of HPCB Micro Metal Gearmotors with extended motor shafts (carbon brushes, not 1000:1) (11MB step)
- 3D model of high-power carbon brush (HPCB) Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors. This diagram does not apply to precious metal brush (i.e. non-HPCB) versions, single-shaft versions, or 1000:1 gear ratios.
- 3D model of 1000:1 HPCB Micro Metal Gearmotors (single-shaft, carbon brushes) (14MB step)
- 3D model of high-power carbon brush (HPCB) Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors with 1000:1 gearboxes. This diagram does not apply to precious metal brush (i.e. non-HPCB) versions, dual-shaft versions, or other gear ratios.
- 3D model of 1000:1 HPCB Micro Metal Gearmotors with extended motor shafts (carbon brushes) (14MB step)
- 3D model of high-power carbon brush (HPCB) Pololu Micro Metal Gearmotors with 1000:1 gearboxes and extended motor shafts. This diagram does not apply to precious metal brush (i.e. non-HPCB) versions, single-shaft versions, or other gear ratios.
Recommended links
- MATLAB script to plot motor performance curves for Pololu brushed DC gearmotors
- This MATLAB script, written by Ali Asgher Mansoor Habiby, plots speed, power, current draw, and efficiency as they vary with torque when you input the gearmotor specifications. It also prints the resistance of the motor, and the current draw and torque at which maximum efficiency and maximum power occur.